Exploration Guide
Learn how Assay helps you discover connections between documents using intelligent theme matching and similarity algorithms.
Web-Based Exploration
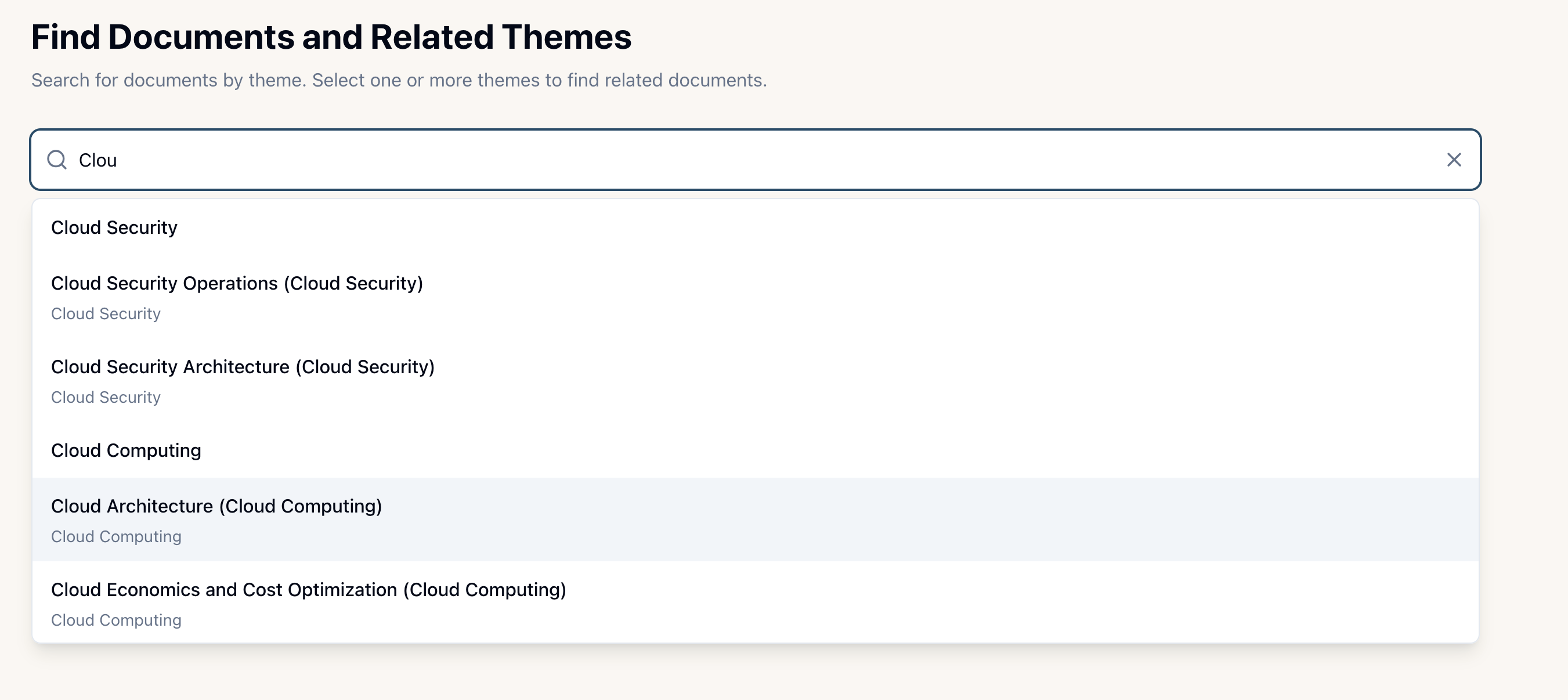
Theme-Based Search
Every document is automatically classified using a canonical theme taxonomy with 180 themes across 30 domains. Use theme search to:
- Browse documents by research area or topic
- Filter search results by specific themes
- Discover related documents through theme overlap
- Explore public collections by theme
Tip: Use fuzzy search to find themes even if you don't know the exact name. The system suggests matches as you type.
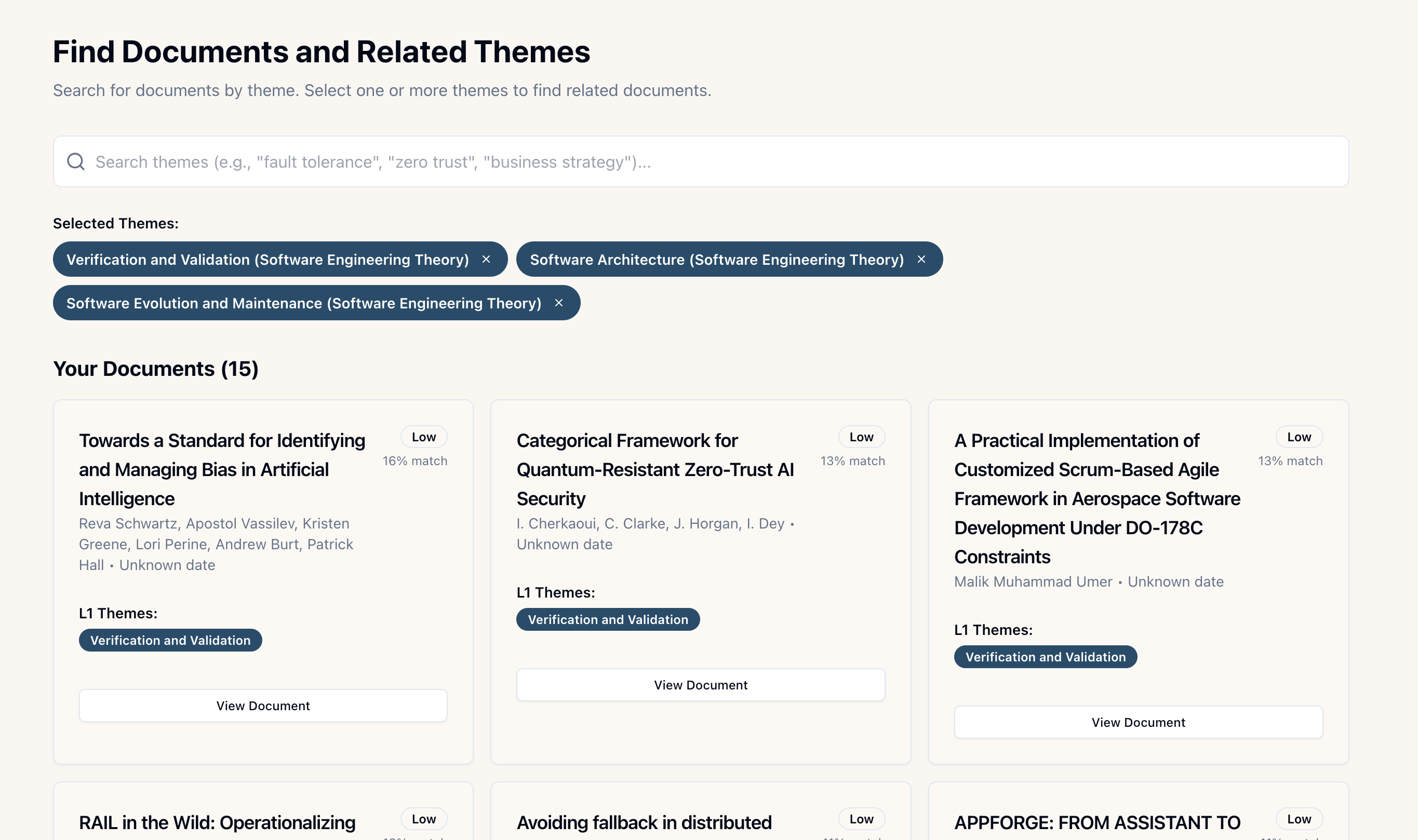
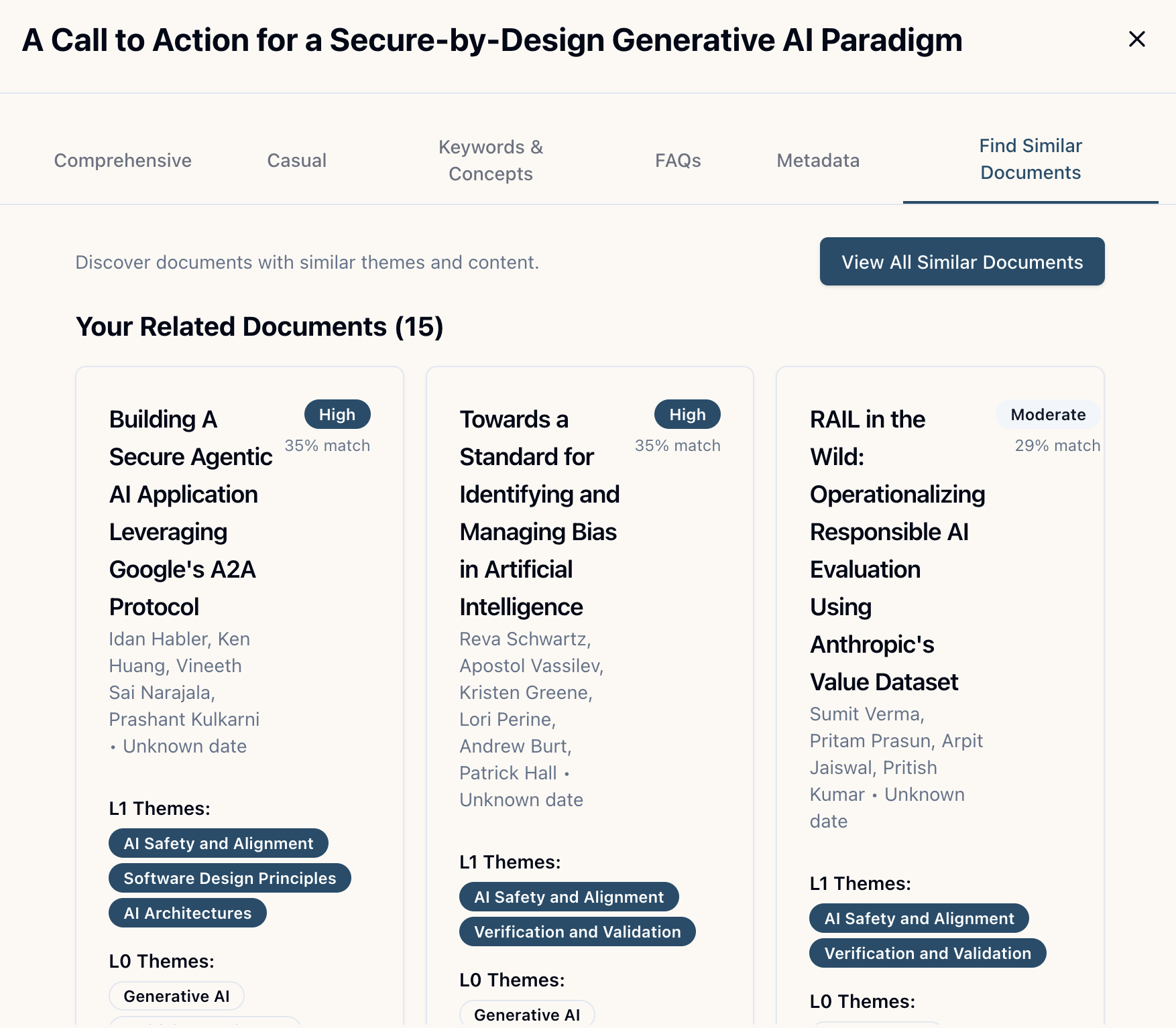
Similar Document Discovery
Find related documents using Jaccard similarity. When viewing a document, click "Find Similar Documents" to see:
- Up to 15 documents from your private collection
- Up to 15 documents from the public collection
- An explanation of why documents matched (which themes overlap)
- Similarity scores sorted by relevance
How it works: The system calculates Jaccard similarity for all documents, then ranks them by weighted score (L1 themes weighted 0.8, L0 themes weighted 0.2).
Library Dashboard
Your personalized dashboard provides theme-based aggregation of your collection:
- View your documents organized by research domains (L0 themes)
- See sub-theme breakdowns (L1 themes) within each domain
- Discover related public documents aligned with your interests
- Get AI-generated insights about your research profile
CLI-Based Exploration
Command-Line Exploration
Explore your collection programmatically with the Assay CLI
The Assay CLI provides programmatic access to all exploration features available in the web interface. Search by theme, find similar documents, and automate research workflows from your terminal.
Key CLI Exploration Commands
Search & Discovery
- • assay documents search
- • assay documents list
- • assay themes list
- • assay documents get <id>
Document Analysis
- • assay documents summary <id>
- • assay documents search --theme
- • Filter: public/personal/private
- • Output: json/table/yaml
Example CLI Workflows
Search by theme:
assay documents search --theme "Competitive Strategy" --filter publicFind similar documents (by theme overlap):
assay documents search --theme ARTIFICIAL_INTELLIGENCE.AI_SAFETY --filter publicDocuments sharing the same theme are inherently similar (Jaccard similarity = 1.0 for exact theme matches)
Generate research report from theme search:
# Find documents → fetch summaries → consolidate
assay documents search --theme "AI Safety" --limit 20 --format json > docs.json
cat docs.json | jq -r '.data[].documentId' | while read id; do
assay documents summary "$id" --type comprehensive >> report.md
doneTip: The CLI uses the same theme taxonomy and similarity algorithms as the web interface. Documents found via --theme share themes (high Jaccard similarity), making them perfect for discovering related research.
Scripting & Automation
Combine CLI commands with shell scripts to automate exploration workflows:
- Batch process documents by theme
- Generate consolidated reports from multiple documents
- Monitor your collection for new documents in specific themes
- Export data for external analysis tools
Example: Theme-based document discovery pipeline
# Discover all documents in a research domain
assay themes list --domain ARTIFICIAL_INTELLIGENCE --format json | \
jq -r '.data[] | select(.documentCount > 0) | .id' | \
while read theme; do
echo "=== Theme: $theme ==="
assay documents search --theme "$theme" --filter public --limit 10
doneMCP-Based Exploration
Exploring with Claude Desktop
Use MCP tools to explore your collection through conversational AI
When using Assay MCP tools with Claude Desktop, you can explore your collection through natural language conversations. Claude uses the same Jaccard similarity algorithm and theme-based organization behind the scenes.
Key MCP Exploration Tools
Search & Discovery
- • search_by_theme - Find documents by canonical theme
- • search_documents - Search by theme, author, or title
- • browse_themes - Explore the theme taxonomy
- • search_by_keywords - Search in keywords and concepts
Similarity & Analysis
- • get_similar_documents - Uses Jaccard similarity
- • compare_documents - Compare up to 10 documents
- • ask_question - Ask questions across your library
- • produce_faq - Generate FAQs from multiple docs
Example MCP Queries
"Find documents similar to this one"
Claude uses get_similar_documents with Jaccard similarity
"What documents share the Cloud Architecture theme?"
Claude uses search_by_theme to find theme matches
"Compare these 3 documents about zero trust"
Claude uses compare_documents to analyze theme overlap and differences
Example: Multi-Theme Document Discovery
Watch Claude use MCP tools to search for documents matching multiple themes, showing the complete workflow from theme browsing to document retrieval and summary access.
When to Use Each Method
Web Interface
Best for:
- Browsing and reading summaries
- Visual exploration of your collection
- Quick theme-based filtering
- Managing document visibility
- Viewing library insights and stats
CLI Tool
Best for:
- Scripting and automation
- Batch processing documents
- Generating reports programmatically
- Integrating with other tools
- Command-line workflows
MCP Integration
Best for:
- Conversational document exploration
- Asking complex questions across documents
- Generating FAQs and comparisons
- AI-powered synthesis and analysis
- Workflow integration with Claude
How Jaccard Similarity Works
Understanding Document Similarity
Documents are related when they share themes, not just keywords
Assay uses the Jaccard similarity coefficient to measure how similar two documents are based on their shared themes. This approach enables semantic discovery—finding related documents even when they use different terminology.
The Jaccard Formula
Jaccard(A, B) = |A ∩ B| / |A ∪ B|
Where A and B are the theme sets of two documents
What this means:
- Intersection (A ∩ B): Themes shared by both documents
- Union (A ∪ B): All unique themes from both documents
- Result: A score between 0 (no overlap) and 1 (identical themes)
Example Calculation
Intersection: [AI, Machine Learning, Deep Learning] = 3 themes
Union: [AI, Machine Learning, Neural Networks, Deep Learning, Computer Vision] = 5 themes
Jaccard similarity = 3/5 = 0.6 (60% similarity)
Why Jaccard?
Theme-Based Matching
Compares documents based on their thematic content, not just keywords. Two documents about "fault tolerance" are related even if they use different terminology.
Normalized Scoring
Provides a consistent 0-1 similarity score regardless of document size. Documents with many themes don't dominate the results.
Hierarchical Awareness
Uses weighted scoring (L1: 0.8, L0: 0.2) to prioritize specific theme matches over broad domain overlap.
Contextual Relevance
Finds documents that share research areas and concepts, enabling semantic discovery across your collection.